Virtualisation – What’s it all about?
Virtualisation – What’s it all about?
In the business and IT world the current buzz word is virtualisation, but why. How does virtualisation help businesses? It’s actually pretty neat and the benefits are explained below; in simple terms.

On-premise Virtualisation
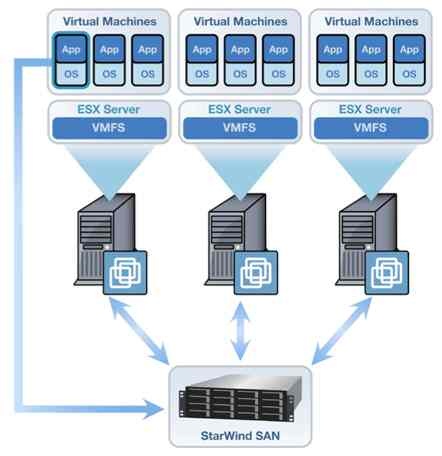
Servers work best when they are designated to a singular task such as web hosting, file management, domain control or remote services. Although servers can simultaneously perform all these tasks, they perform so much better when they are focussed on only one. This is where virtualisation has changed things. Individual virtual servers can be created for each role required by a business, and they all reside on the physical server with network, storage and processor resources divided up between the virtual servers.
This can be achieved through the use of virtualisation software such as VMWare, Microsoft Hyper V, Citrix and many others. Once this software has been installed on a physical device, a companies entire infrastructure can be created inclusive of desktops; all without the need to buy more hardware. That is unless the business grows exponentially; resources on physical devices are not infinite.
The use of a Storage area Network (SAN) is a popular choice of physical device as it pools storage from a number of hard drives. It then separates the storage into Logical Unit Numbers (LUN) which virtual machines can use. I will not explain how it does this as our target audience will, I’m sure, lose interest.
Advantages of Virtual Servers:
- Virtual servers free up space within offices which can help reduce rental costs or free up space for team members.
- They are centrally managed.
- Greater availability and easier recovery in case of disaster.
- The ability to run backups and use multiple operating system environments on the same computer..
- Servers can be migrated to new hardware transparently.
- Virtual servers can increase reliability as the failure of software does not affect the other services.
- Cost reduction is possible using small virtual servers on a more powerful single server.
- Virtualisation software reallocates hardware resources dynamically between one virtual machine and another.
- Load balancing.
- Support for legacy applications.
- Reduction of personnel, power, and cooling costs by using less physical equipment.
Disadvantages of Virtual Server:
- A major disadvantage of virtual servers is if the server goes offline, all the websites hosted by it will also go offline.
- Virtual environments need to be monitored, configured and saved.
- Indirect access to hardware, for example, specific cards or USB devices.
- There are no consolidated methods to measure the performance of virtualised environments.
- When several virtual machines are running on the same host, performance maybe hindered if the device it’s running on lacks sufficient power.
- There is significant RAM consumption since each virtual machine will occupy a separate area of the same memory.
- It requires multiple links in a chain that must work together cohesively.
Currently, the advantages only slightly outweigh the disadvantages, however, developments in this area will eventually reduce physical server utilisation. This means the industry will increasingly move towards Virtualisation and a virtual infrastructure to support their business requirements.
If you have any questions relating to virtualisation, please contact CCSW today.




